责任链模式
Overview
顾名思义,责任链模式(Chain of Responsibility Pattern)为请求创建了一个接收者对象的链。
这种模式给予请求的类型,对请求的发送者和接收者进行解耦。
这种类型的设计模式属于行为型模式。
在这种模式中,通常每个接收者都包含对另一个接收者的引用。
如果一个对象不能处理该请求,那么它会把相同的请求传给下一个接收者,依此类推。
主要解决
职责链上的处理者负责处理请求,客户只需要将请求发送到职责链上即可,无须关心请求的处理细节和请求的传递,所以职责链将请求的发送者和请求的处理者解耦了。
何时使用
想在访问一个类时, 进行一些控制
应用实例
优点
- 降低耦合度。它将请求的发送者和接收者解耦
- 简化了对象。使得对象不需要知道链的结构
- 增强给对象指派职责的灵活性。通过改变链内的成员或者调动它们的次序,允许动态地新增或者删除责任
- 增加新的请求处理类很方便。
实现
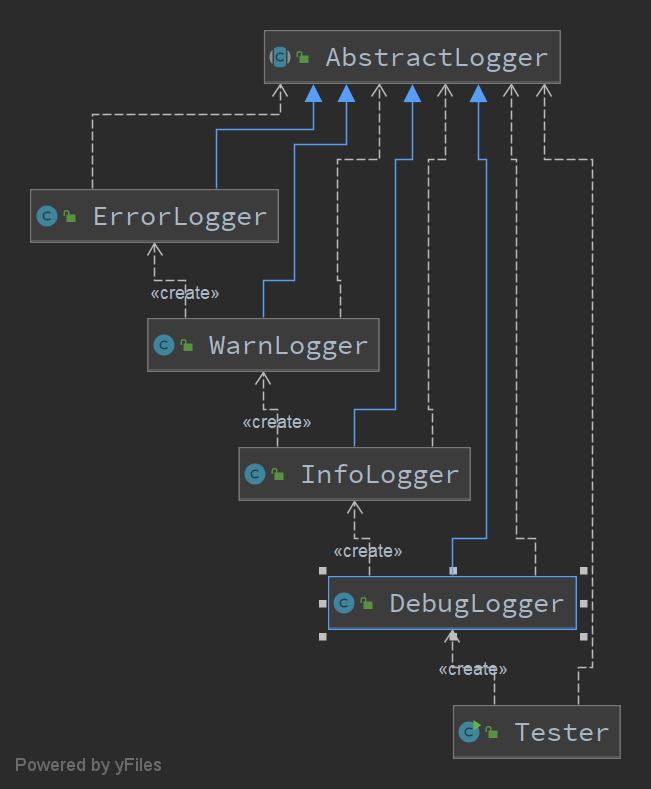
Logger
AbstractLogger
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| package individual.cy.learn.pattern.behavioral.chain4responsibility;
/**
* @author mystic
*/
public abstract class AbstractLogger {
public final static int DEBUG = 1;
public final static int INFO = 2;
public final static int WARN = 3;
public final static int ERROR = 4;
protected int level;
protected AbstractLogger nextLogger;
public void setNextLogger(AbstractLogger nextLogger) {
this.nextLogger = nextLogger;
}
public void logMessage(int level, String message) {
// if no ability to handle, hand up it to successor
if (this.level == level) {
write(message);
} else {
if (nextLogger != null) {
nextLogger.logMessage(level, message);
}
}
}
/**
* write log
*
* @param message log info
*/
protected abstract void write(String message);
}
|
DebugLogger
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| package individual.cy.learn.pattern.behavioral.chain4responsibility;
/**
* @author mystic
*/
public class DebugLogger extends AbstractLogger {
public DebugLogger() {
this.level = AbstractLogger.DEBUG;
setNextLogger(new InfoLogger());
}
@Override
protected void write(String message) {
System.out.println("DebugLogger.write: " + message);
}
}
|
InfoLogger
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| package individual.cy.learn.pattern.behavioral.chain4responsibility;
/**
* @author mystic
*/
public class InfoLogger extends AbstractLogger {
public InfoLogger() {
this.level = AbstractLogger.INFO;
setNextLogger(new WarnLogger());
}
@Override
protected void write(String message) {
System.out.println("InfoLogger.write: " + message);
}
}
|
WarnLogger
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| package individual.cy.learn.pattern.behavioral.chain4responsibility;
/**
* @author mystic
*/
public class WarnLogger extends AbstractLogger {
public WarnLogger() {
this.level = AbstractLogger.WARN;
setNextLogger(new ErrorLogger());
}
@Override
protected void write(String message) {
System.out.println("WarnLogger.write: " + message);
}
}
|
ErrorLogger
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| package individual.cy.learn.pattern.behavioral.chain4responsibility;
/**
* @author mystic
*/
public class ErrorLogger extends AbstractLogger {
public ErrorLogger() {
this.level = AbstractLogger.ERROR;
setNextLogger(null);
}
@Override
protected void write(String message) {
System.out.println("ErrorLogger.write: " + message);
}
}
|
Tester
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| package individual.cy.learn.pattern.behavioral.chain4responsibility;
/**
* @author mystic
*/
public class Tester {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AbstractLogger debugLogger = new DebugLogger();
System.out.println("**************************");
debugLogger.logMessage(1, "Here is a debug message.");
System.out.println("==========================");
debugLogger.logMessage(2, "Here is a info message.");
System.out.println("==========================");
debugLogger.logMessage(3, "Here is a warn message.");
System.out.println("==========================");
debugLogger.logMessage(4, "Here is a error message.");
System.out.println("==========================");
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| **************************
DebugLogger.write: Here is a debug message.
==========================
InfoLogger.write: Here is a info message.
==========================
WarnLogger.write: Here is a warn message.
==========================
ErrorLogger.write: Here is a error message.
==========================
|
