解释器模式
Overview
解释器模式(Interpreter Pattern)提供了评估语言的语法或表达式的方式,它属于行为型模式。
这种模式实现了一个表达式接口,该接口解释一个特定的上下文。
这种模式被用在 SQL 解析、符号处理引擎等。
主要解决
对于一些固定文法构建一个解释句子的解释器
何时使用
如果一种特定类型的问题发生的频率足够高,那么可能就值得将该问题的各个实例表述为一个简单语言中的句子。
这样就可以构建一个解释器,该解释器通过解释这些句子来解决该问题。
应用实例
优点
- 可扩展性比较好,灵活
- 增加了新的解释表达式的方式
- 易于实现简单文法
实现
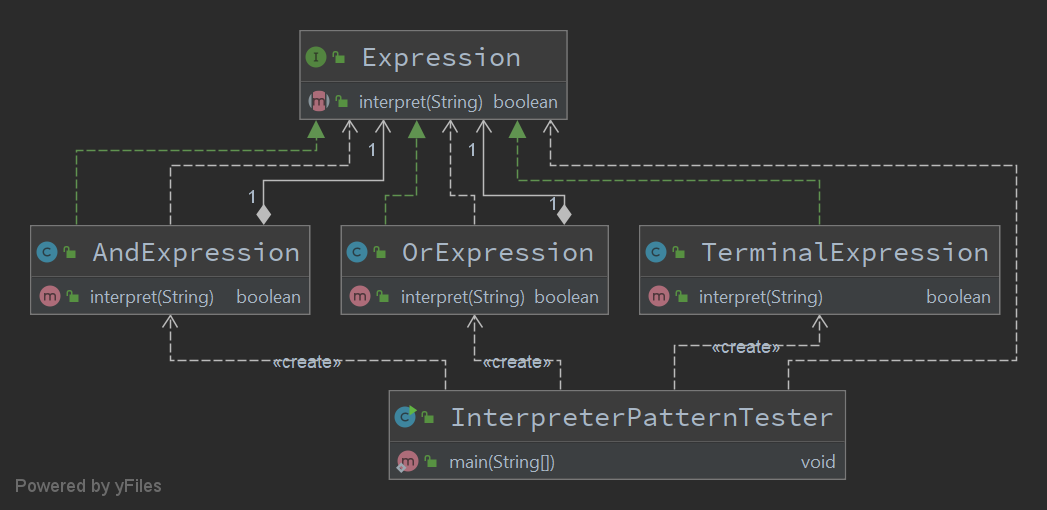
Expression
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| package individual.cy.learn.pattern.behavioral.interpreter;
/**
* @author mystic
*/
public interface Expression {
/**
* interpret
*
* @param context context
* @return true or false
*/
boolean interpret(String context);
}
|
TerminalExpression
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| package individual.cy.learn.pattern.behavioral.interpreter;
/**
* @author mystic
*/
public class TerminalExpression implements Expression {
private final String data;
public TerminalExpression(String data) {
this.data = data;
}
@Override
public boolean interpret(String context) {
return context.contains(data);
}
}
|
AndExpression
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| package individual.cy.learn.pattern.behavioral.interpreter;
/**
* @author mystic
*/
public class AndExpression implements Expression {
private final Expression exp1;
private final Expression exp2;
public AndExpression(Expression exp1, Expression exp2) {
this.exp1 = exp1;
this.exp2 = exp2;
}
@Override
public boolean interpret(String context) {
return exp1.interpret(context) && exp2.interpret(context);
}
}
|
OrExpression
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| package individual.cy.learn.pattern.behavioral.interpreter;
/**
* @author mystic
*/
public class OrExpression implements Expression {
private final Expression exp1;
private final Expression exp2;
public OrExpression(Expression exp1, Expression exp2) {
this.exp1 = exp1;
this.exp2 = exp2;
}
@Override
public boolean interpret(String context) {
return exp1.interpret(context) || exp2.interpret(context);
}
}
|
Tester
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| package individual.cy.learn.pattern.behavioral.interpreter;
/**
* @author mystic
*/
public class InterpreterPatternTester {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// rule: Kushagra and Lokesh are both male.
Expression person1 = new TerminalExpression("Kushagra");
Expression person2 = new TerminalExpression("Lokesh");
Expression isSingle = new OrExpression(person1, person2);
// rule: Vikram is committed.
Expression vikram = new TerminalExpression("Vikram");
Expression committed = new TerminalExpression("Committed");
Expression isCommitted = new AndExpression(vikram, committed);
System.out.println(isSingle.interpret("Kushagra"));
System.out.println(isSingle.interpret("Lokesh"));
System.out.println(isSingle.interpret("Achint"));
System.out.println(isCommitted.interpret("Committed, Vikram"));
System.out.println(isCommitted.interpret("Single, Vikram"));
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
| true
true
false
true
false
|
